Burkitt lymphoma (BL)
- Method:
- Anticoagulant:
- Recommendation:
- Method:Cytomorphology
- Anticoagulant:EDTA
- Recommendation:obligatory
- Method:Immunophenotyping
- Anticoagulant:EDTA or Heparin
- Recommendation:obligatory
- Method:Chromosome analysis
- Anticoagulant:Heparin
- Recommendation:facultative
- Method:FISH
- Anticoagulant:EDTA or Heparin
- Recommendation:obligatory*
- Method:Molecular genetics
- Anticoagulant:EDTA or Heparin
- Recommendation:facultative
*As test material for the FISH analysis we recommend unfixed, unstained smears
Burkitt lymphoma (BL) is one of the aggressive lymphomas and is characterized by an extraordinarily high cell division rate of B cells. Based on current guidelines and the current state of research, there are various diagnostic recommendations for patients with Burkitt lymphoma. We have summarized the most important information on the classification and diagnostic methods at MLL. In addition, we provide further information on prognosis and therapy in Burkitt lymphoma.
Burkitt lymphoma: Classification
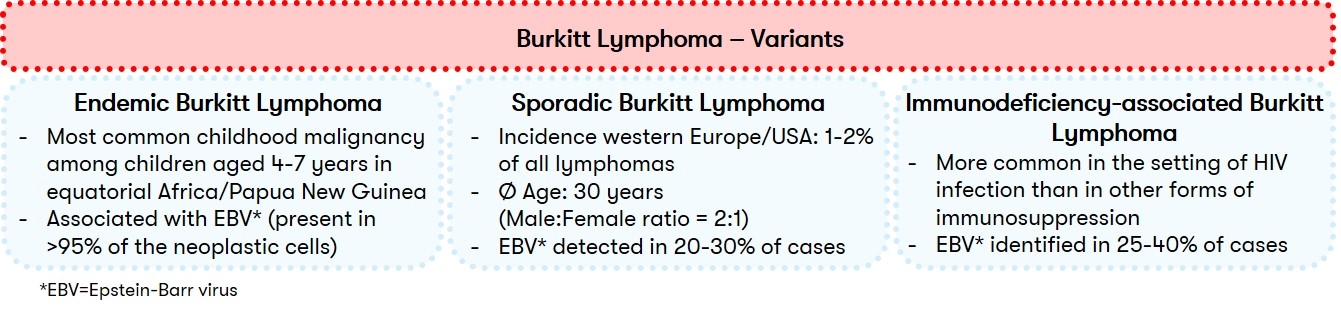
The WHO distinguishes between different subtypes of Burkitt's lymphoma (BL). Traditionally, the clinical variants of endemic BL, sporadic BL, and immunodeficiency-associated BL are distinguished (Fig. 1). However, since 2022, WHO has recommended that subtypes be differentiated into EBV-associated BL and EBV-negative BL according to the concurrent presence of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) (WHO 2022). This distinction emphasizes the biological heterogeneity of the disease (López et al. 2022).
Burkitt lymphoma: Diagnostic methods and their relevance
Since there is no method that represents the sole gold standard in the diagnosis of Burkitt lymphoma, an integrated diagnostic approach taking into account morphology/histology, immunophenotype, and genetics is central. Due to the frequent CNS involvement, an additional cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) examination should be performed.
Burkitt lymphoma: Prognosis and therapy
The prognosis of BL patients treated with modern immunochemotherapy regimens including rituximab is excellent in resource-rich settings. Overall survival here is over 80% in adults and over 90% in children in recent multicenter studies. In low-to-moderate resource countries, prognosis is less good. This is partly due to inadequate facilities for diagnosis and treatment, and insufficient awareness of the disease among the population and health care workers (López et al. 2022, WHO 2022).
Risk assessment of patients with Burkitt lymphoma can be assisted by the BL-IPI (BL International Prognostic Index), which analyzes various clinical parameters (Olszewski et al. 2021) that also have prognostic significance in HIV-associated BL (Alderuccio et al. 2021).
Therapeutic options for Burkitt's lymphoma can be found in a recent review by Crombie and LaCasce, among others (Crombie & LaCasce 2021) and Malfona et al. (Malfona et al. 2024).
Status: June 2024