Chronic eosinophilic leukemia (CEL)
- Method:
- Anticoagulant:
- Recommendation:
- Method:Cytomorphology
- Anticoagulant:EDTA
- Recommendation:obligatory
- Method:Immunophenotyping
- Anticoagulant:EDTA or Heparin
- Recommendation:obligatory
- Method:Chromosome analysis
- Anticoagulant:Heparin
- Recommendation:obligatory
- Method:FISH
- Anticoagulant:EDTA or Heparin
- Recommendation:obligatory
- Method:Molecular genetics
- Anticoagulant:EDTA or Heparin
- Recommendation:obligatory
Based on the current guidelines and the current state of research, there are different diagnostic recommendations for patients with chronic eosinophilic leukemia (CEL). We have summarized the most important information on the classification and diagnostic methods at MLL. In addition, we provide further links and literature on prognosis and therapy in CEL, so that you can inform yourself in more detail.
Chronic eosinophilic leukaemia: Classification
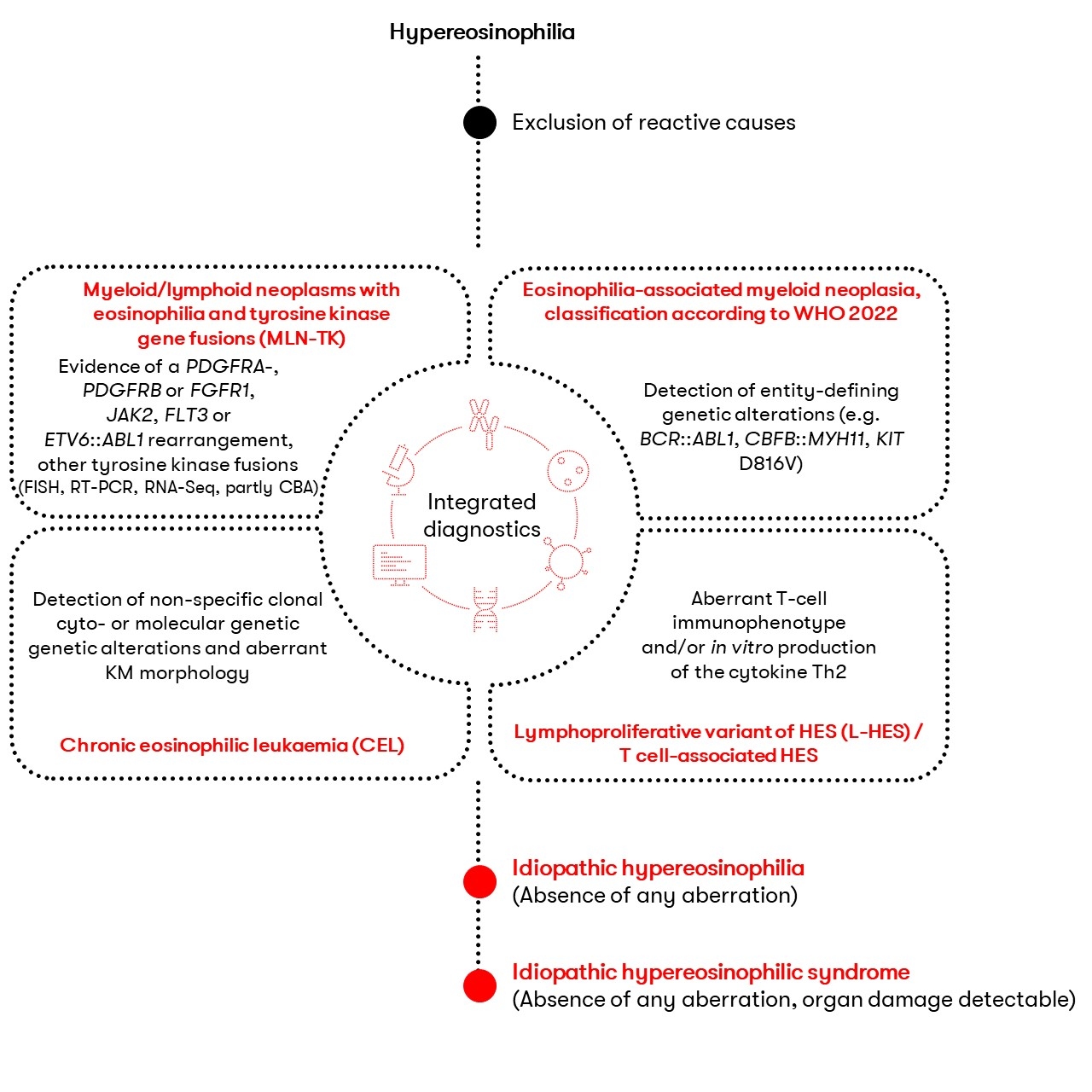
Chronic eosinophilic leukemia (CEL) is characterized by clonal eosinophilia and is classified as a myeloproliferative neoplasm (MPN). It is a very rare and aggressive disease in which clonal proliferation of eosinophil progenitor cells causes an increase in eosinophils in peripheral blood, bone marrow, and peripheral tissues. Leukemic infiltration or release of cytokines, enzymes, or other proteins from the eosinophils can lead to organ damage of, for example, the heart, lungs, skin, gastrointestinal tract, or central nervous system (WHO 2022).
The diagnosis of CEL is usually made by excluding other hematologic neoplasms that may present with eosinophilia. The following criteria apply according to WHO 2022 for establishing the diagnosis (WHO 2022):
- Eosinophilia (eosinophilic count >1,5 x 109/L) in peripheral blood for at least two examinations over an interval of at least 4 weeks
- WHO criteria for MPN, MDS/MPN, MLN-eo, mastocytosis or AML are not met
- There is no PDGFRA, PDGFRB or FGFR1 rearrangement, no ETV6::ABL1 rearrangement and no JAK2 and FLT3 rearrangements
- Clonal cyto- or molecular genetic alteration is present (the possibility of clonal hematopoiesis of indeterminate potential (CHIP) should be considered)
- There is an aberrant morphology in the bone marrow (e.g., megakaryocytes or erythroid dysplasia)
If clonality cannot be demonstrated by detection of a cyto- or molecular genetic alteration, a diagnosis of idiopathic hypereosinophilic syndrome (HES) should be made. This is characterized by an eosinophil count of ≥1.5 x 109/L persisting for ≥4 weeks for which no underlying cause can be demonstrated. In addition, signs of organ involvement and dysfunction are present. Without these signs, the term idiopathic hypereosinophilia should be used. Eosinophilia may also be caused by the increased release of T-cell-associated cytokines. Therefore, the presence of aberrant T-cells should be excluded. An overview of the differential diagnosis is given in Figure 1.
CEL: Diagnostic methods and their relevance
CEL: Prognosis and therapy
An unfavorable prognosis has been described for CEL and transformation to acute leukemia is possible. According to WHO, an abnormal karyotype, atypical megakaryocytes, thrombocytopenia, and bone marrow fibrosis are considered potential unfavorable prognostic markers (WHO 2022).
Since CEL is a very rare entity and diagnosis is sometimes difficult, studies to date include only a small number of patients, which is why no precise prognostic factors and standardized treatment strategies are available. An overview of possible approaches is provided in the Onkopedia guideline Eosinophilie: Primäre klonale Eosinophile und Differentialdiagnosen.
Status: December 2023